Formation of Images on a concave mirror: When an object is placed at different positions in front of a concave mirror, various types of images are formed, which can clearly understood by considering following situations:
1) Object place in between pole and focus: :-When the object is placed in between the pole and principle focus of a concave mirror, the image is formed behind the mirror, the image formed is virtual , erect and magnified i.e., larger in size than those of the object as shown under:-
2) Object at focus: When the object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is at infinity highly magnified, real and inverted as shown Under
3) Object between focus and centre of curvature:- When the object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image is formed beyond the centre of curvature. The image formed is real, inverted and magnified in size of the object as shown under:-
4) Object at centre of curvature:- When the object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is also at centre of curvature, same in size, real and inverted as shown under:-
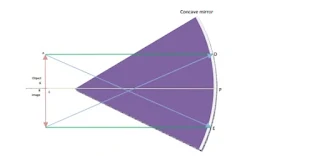
5) Object beyond centre of curvature:- When the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature, the image formed is in between the focus and centre of curvature, the image is smaller is size than the object (diminished), real and inverted.
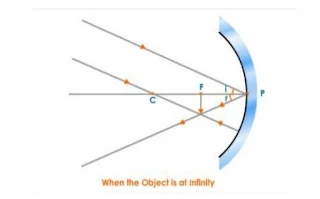
6) Object at infinity:- When the object is placed at the infinity form the concave mirror , the image formed is at the focus, highly diminished, real and inverted as shown under:
Rules for obtaining Images on a convex mirror:-
The various rules employed for obtaining images on a convex mirror are:-
1:-A ray of light parallel and close to the principle axis of a convex mirror appears to be coming from its focus after reflection from the mirror.
2:- A ray of light going towards the centre of curvature of a convex mirror is reflected along its own path.
Images formed by a convex mirror: The image formed by a convex mirror does not depends upon the position and size of the object. It always forms the image behind the mirror, and in between the pole and the focus. The image formed is however always virtual, erect and diminished as shown under:-
Mirror formula:- A formula which indicates the relationship between the image distance, object distance and focal length of a mirror is known as the mirror formula which can be written as under:-
1 /image distance + 1/object distance = 1 /object distance
If the image distance of a mirror be represented by u and the focal length by f, then mirror formula
can be represented as under:-
1/u . + 1/v . = 1/f
Where v = distance of the image from the mirror.
And u = object distance from the mirror.
Also f = focal length of the mirror
Linear magnification of a mirror:- Linear magnification of a mirror is the ratio of height of the image to the total height of the object, thus, Linear magnification = Height of Image / Height of Object
If “h1” be the height of the object placed in from t of a mirror and if “h2” be the image formed , the n
linear magnification “M” produced by the mirror can be represented as under:-
M = h2 / h2
However linear magnification of a mirror is also equal to the ratio between image distance and object distance form a mirror but with negative sign as represented as under:-
M = - v/u
Where v = Image distance
And u = object distance of a mirror.
If the magnification has a positive (plus) sign, the n the image formed will be virtual and erect and if it has a negative (minus) sign, the image formed will be real and inverted.
Uses of a concave mirror:-
The various uses of a concave mirror are as under:-
It is used as shaving and dressing mirror.
It is used as a reflector in car headlights, torches, table lamps and searchlights etc.
The opticians to concentrate light on the specific body parts during treatment.
It is also used in the solar heating devices to focus the solar radiation e.g., solar cookers.
It is used as object lens in telescopes.
Uses of a convex mirror:-
the important uses of convex mirror are:-
It is used in rear view mirrors in motor vehicles to see traffic at the backside, because it always produces and erect and diminished image of the object. It also has a very wide field of view, which helps a driver to have a clear view of the traffic behind.
Lens :- A lens is a piece of transparent glass bounded by two spherical surfaces. It is of two main types viz.
1. Concave Lens:- A lens having both of its surfaces curved inwards is called as a concave lens. It is thin in the middle and thicker at the edges. It is also called as a diverging lens as it diverges a parallel beam of light rays incident on it.
Kinds of concave lenses:- these are of three kinds as explained under in the diagram:-
2. Convex Lens:- A lens having both of its surfaces bulged outwards is called as a convex lens. It is thicker at the middle and thin at the edges as shown under. It is also called as converging lens, as it converges a parallel beam of light rays.
Terms associated with Lenses:- the various terms associated with the lenses (concave and convex) are:-
(i) Optical centre :- the central point of a lens (concave or convex) is called as its optical centre. It is represented by letter “C” and has the property that it allows light ray to pass through it without any deviation.
(ii) Principle Axis:- The principle axis of a lens is a line that passes through the optical centre of the lens and is perpendicular to both of its faces.
(iii)Principle focus:- (a) Concave Lens :- the principle focus of a concave lens is a point on its principle axis from which light rays, originally parallel to the axis, appears to diverge after passing through the lens has a virtual focus represented by letter F’
Principle focus:- (b) Convex Lens :- The principle focus of a convex lens is a point on its principle axis to which light rays originally parallel to the principle axis converge after passing through it. A convex lens has a real focus represented by letter f.
Sign convention for Lenses:-( V.V.imp)
The various sign conventions used for measuring distances in the ray diagram of lenses are:-
- All distances are measured from the optical centre of a lens.
- The distances measured in the same direction of that of incident light are taken as positive.
- The distances measured against the direction of the incident light are taken as negative.
- The distances measured upwards and perpendiculars to the principle axis are considered as positive.
- The distance measured downwards and perpendiculars to the principle axis are considered as negative.
Rules for Images formed by a convex Lens:- The various rules employed for obtaining images on
a convex lens are listed as under:-
1:-An incident ray of light passing through the optical centre of a convex lens emerges undeviated after refraction through the lens.
2:-An incident ray of light parallel to the principle axis of a convex lens passes through the focus after refraction.
An incident ray of the light passing through the focus of a convex lens becomes parallel to the principle axis after refraction.
Formation of Images on a convex Lens:- When an object is placed at the different positions in
front of a convex lens, various types of images are formed, which are described as under:
1) Object placed between C and F1:- When an object is placed between the optical centre and focus of a convex lens, the image formed lies behind the object on the same side. The image formed is virtual, erect and magnified i.e., larger in size than the size of the object
2) Object placed at the F1:- When an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, the image is formed at infinity , which is real , inverted and highly enlarged i.e., larger in size than the object as shown under:-
3) Object placed between F1and 2F1
:- When an object is placed between the focus and 2F in from of a convex lens, the image formed lies beyond 2f. the image formed is real, inverted and larger in size than of the object as shown under:-
4) Object placed at 2f1:- When an object is placed at 2f/ in form of a convex lens. The image is formed at 2f on the other side of the lens, which is real , inverted and of the same size of the object as shown under:-
5) Object place beyond 2f1:- When an object is placed beyond 2f in front of a convex lens, the image is formed between F and 2F on the other side of the lens which is real, inverted and diminished i.e., smaller in size than the size of the object as shown under:
6) Object at Infinity:- When an object is at infinity from a convex lens, the image formed lies at the focus, which is real, inverted and highly smaller in size that the size of the object as shown under:-
Power of Lens:- The power of a lens may be defined as the reciprocal of its focal length expressed in maters. It is represented by letter “p”. thus Power of lens = 1 Or P =f1
Where P = Power of lens
And F = focal length of the lens.
The S.I unit of power of a lens is dioptre, which is denoted by letter ”D”. The power of a lens is said to be one dioptre, if its focal length is equal to 1 meter. However a convex lens has a positive focal length and a concave lens has a negative focal length, thus a convex lens has a positive power and a concave lens ahs a negative power.
Lens Formula:- The formula which gives a relationship between the image distance, object distance and the focal length of a lens is referred to as Lens formula. If “u” be the object distance and “v” as the image distance and “f” as focal length of a lens, then the lens formula can be given as under :- 1 - 1 = 1 Image distance Object distance Focal length Or v1u1 = f1
Linear Magnification of a Lens:- it is defined as the ration between the height of image to the height of object. If “h2”be the height of object and if “h1” be the height of image, then the magnification “M” of a lens can be given as : Magnification = Height of image Height of object Or M = h2 h1
Where h2 = height of image and h1 = height of object. However the ratio of image i\distance to object distance is also known as magnification. If “u” be distance of object and “V” as distance of image from a lens, the n magnification “M” of a lens can be given asunder :-
Magnification = Image distance Height of object Or M = V U
Where v = Image distance
And U = object distance
However , if M has a positive sign then the image formed is virtual and erect and if it has a negative sign, then the image formed will be real and inverted.
Rules for image formation by a concave lens:-
1:-An incident ray parallel to the principle axis of concave lens appears to be coming from its focus after refraction through the lens.
2:-An incident ray passing through the optical centre of a concave lens goes straight without any deviation from its straight a path.
Image formation by a concave lens:- formation of images on a concave lens does not depends upon position of the object in from of a concave lens. A concave lens always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image i.e., smaller in size than the size of the object,.....
FOR FIRST PART CLICK ON THE LINK BELOW
https://jkgovtschoolnotes.blogspot.com/2022/01/class-10-physics-light-reflection-and.html
FOR SECOND PART CLICK ON LINK BELOW
https://jkgovtschoolnotes.blogspot.com/2022/01/class-10-physics-light-reflection-and.html
























1 Comments
One of the best.Good going sir
ReplyDelete