 |
| Eye anatomy |
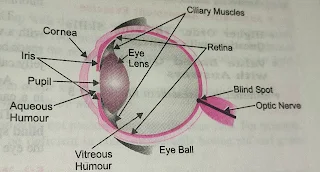
Structure of Human eye
The eye is the most important organ in the human body. It is associated with vision and acts as a key Optical instrument. The human eye is embedded in to two sockets of skull . It is spherical in shape.
Externally a thick, , opaque layer covers the eye called as sclerotic. The human eye is most important. organ in human body . This organ is used to see the beautiful nature and natural phenomena. The main parts of the eye and their The functions are as follows:
cornea
It is the transparent part of the eye and allows light to enter in to it .cornea is also called as window or aperture of the eye.
Iris
This is a round diaphragm with a hole in the centre, This hole is called a pupil . It has Circular diaphragm contains muscles and pigments. The colour of the eyes depends on their colour. The job of the iris is to control the amount of light entering in to the eye . Bright light makes the pupil smaller, However, when dimmed, it widens.
Lens
The eye lens is a crystal line double convex lens and is made of transparent and flexible tissue. it is behind the pupil held by citify muscles. It focuses the images of an objects on the Retina.
Ciliary muscles
These muscles hold the lens in position. The ciliary muscles controls the focal length of the Eye lens. When these muscles contract, the focal length of the lens increases. on the other hand, When they expand, they put pressure on the lens of the eye and reduce the focal length of the lens.
Retina
It acts as a screen to capture the image of the object. It has the number of cells in its shape. Rods and cones that are sensitive to light. These cells convert light energy into nerve impulses Or Signals
Optic nerve
The optic nerve is made up of nerve fibres coming from the retina. It takes the nerves. Emotions or gestures to the brain. The brain finally interprets signal signals in to appropriate action
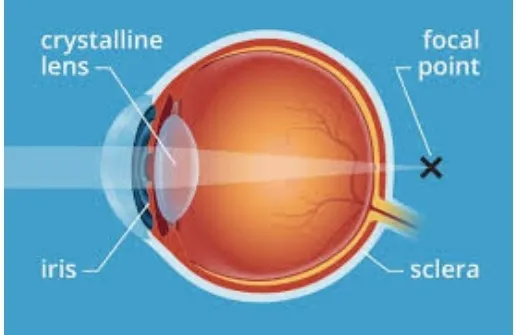
Working of an eye
Rays of light are reflected from the surfaces of objects and these rays on entering in to the eye through the pupil fall on Convex lens or eye lens. It converges these Rays of light and create a real and inverted image on the yellow spot of the retina ,
The image formed on the retina is then turned into nerves impulse and Send to the brain through optic nerves, Which gives rise to the sense of sight. The sense of sight produced is correct and Complete and reverse image showed no effect Formed on the retina. However, the amount of The light rays entering the eye are controlled By Iris. By adjusting its pupil size. If The amount of light rays on the eye is high. The pupil reduces its size and thus decreases. The intensity of light As the light diminishes, the size of the pupil increases. Provide adequate access to light.
Accommodation
A normal eye can see distant objects as well as near objects. It happens with the help of Ciliary muscles, which change the thickness as well as the focal length of the lens of an eye. As a result of This ability of an eye to focus on distant objects as well as near objects by converging power of its lens is called accommodation. The accommodation strength of a normal eye varies between infinity to 25 cm, that means, a normal eye can see an object at 25 cm also it can see object at infinity.
Defects of vision
The human eye has various defects such as myopia. Hypermetropia presbyopia, Commonly found defects such as Astigmatism and cataract these are described as under:-
Myopia:-short Sightness
Myopia is usually an eye disorder that causes a person unable to see distant objects clearly, although it can see near objects. This defect is due to high converging power of the lens of the eye, which is created from insufficient relaxation of the ciliary muscles as a result the image of The distant object is not formed in front of the retina.
However, this defect can be corrected by the use of concave lenses. Due to which Incidental light rays come from a distant object help the lens to focus the image in the right spot on Retina so that the eyes can see clearly.
Hypermetropia (long sightless) :-
Hypermetropia is an eye defect in which the eye cannot see near by objects perfectly even though it can see distant objects clearly. This defect is due to a low converging power of the lens which is mainly due to the weakening of the celery muscles, resulting in Decreased muscle capacity. Due to the low converging power of the eye lens, the image of the nearby object is corrected by using spectacles containing convex lenses, which converges the incident light rays from a nearby object and helps the eye lens in forming the image at the right spot of the Retina. So that an eye can see it clearly

Presbyopia
A human eye which cannot see the near object as well as far off (or distant) objects clearly is said to suffer from a defect known as Presbyopia. This defect arises due to the ageing of a person. The ciliary muscles are weakened and the flexibility of the crystalline lens of the human eye decreases with age of the personal. As a result, human eye is unable to see the near as well as distant objects clearly.
Correction of presbyopia
This error can be corrected with a bifocal lens. A two focal lens consists of a concave lens on The upper surface of the bifocal lenses and the convex lens form the lower surface of the bi focal lenses.
The upper surface of the bi focal lenses (i.e concave lenses) enables man to see distant objects clearly. The lower surface of the bi focal lenses (i.e the convex lens) enables man to see things up close.....
Dispersion of white light by glass prism
When the white light passes through the glass prism, we find a band of seven colours on the white screen. The colours on the screen are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. These colours. Can be Remembered as VIBGYOR. From this observation we can conclude that white light is a mixture of seven colours. Dividing white light into seven colours is called Dispersion of light...
Cause of dispersion
White light consists of seven colours: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. every colour. Has Its own wavelength. The red colours wavelength is the longest and the violet colours wavelength is the shortest.
the speed of light or colour depends up on the Wavelength larger the wave length greater is the speed of colour , thus, each colour of light travels at a given speed in a given medium. speed of red is greater than the speed of orange in a medium. Orange is faster than the Yellow colours and so on. Therefore, the speed of red in a medium is the highest and Violet colour has the lowest speed. Therefore, all colours of white light are reflected in different amounts as they pass. Through a glass prisms . Therefore, when a white light passes through a glass prism , the different components of white light Come out of the prism at different angles. This leads to the spread of white light. Or Dispersion
Range of vision
The maximum distance within which the normal eye can focus on a different object is called the range of vision.
It varies from infinity to 25 centimetres', meaning that a normal human eye can clearly focus on objects. Lying Between infinity to 25 cm.
Atmospheric Refraction
When Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it constantly moves from the rare to the dense medium.
And because of this the light is resilient. This is called the elasticity of light in the atmosphere. Or Atmospheric refraction
Twinkling of stars
The light emitted from the stars travels through the Earth's atmosphere before reaching Our eyes , As we know Earth's atmosphere is not the same it consists of many layers of different densities. dense near the surface of the earth. As we go from top to bottom, the density of the layers and The reflex index gradually decreases. As light from a star enters the uppermost layer of the atmosphere, it leans towards normal. And This process continues until the light enters our eyes so due to refraction the apparent position of the star to us is different from the actual position of the star.
Furthermore, different layers of the atmosphere are dynamic due to rise in temperature the density of The layers of the atmosphere are continuously changing. Therefore, the apparent position of the star is constantly changing to us Leads to the brightness Or dimness of a star. A change in the intensity of the light entering our eyes due to a change in The apparent position of the star leads to constant flickering and twinkling of the star.
We see sun for few minutes even after it has set. Why
The sun sets when it is below the horizon in the evening. Light rays from the sun below the horizon reach our eyes due to the refraction of light. the rays seem to come from the apparent position of the sun which is above the horizon. Therefore, we can see the sun. for a few minutes (about 2 minutes) even after it has set.
Similarly, the sun rays can be seen around 2 minutes. before it really goes up. Or rises up in this way , we gain about 4 minutes of additional daylight each day. 2 minutes at the time sunrise and 2 minutes at the time of sun set
 |
| Advance sunrise |
 |
| Delayed sunset |
Why is the colour of clear sky blue?
When sunlight enters the earth’s atmosphere the atoms or molecules of the gases present in the atmosphere scatter this light. Since wavelength of red colour is larger than the wavelengths of other colours in sunlight, so red colour is scattered the least. Violet colour is scattered the most followed by blue, green, yellow, orange and red colours respectively. Our eye is more sensitive to the blue light than the violet light. Therefore, scattered light in the sky contains blue colour in plenty and hence the clear sky appears blue to us
Why sunset and Sunrise are Red?
At the time of sunrise or sunset, the position of the sun is very far away from us. The sunlight travels longer distance through the atmosphere of the earth before reaching our eyes. Scattering of blue light is more than the scattering of red light. As a result of this, more red lights reaches our eyes than any other colour. Hence sunset and sunrise appear red.
Tyndall Effect
The scattering of light by particles in its path is called Tyndall effect.
When a beam of sunlight enters a dusty room through a window, then its path becomes visible to us. This is because the tiny dust particles present in the air of room scatter the beam of light all around the room. And when this scattered light enters our eyes, we can see the beam of light. Thus, an example of Tyndall effect is the way a beam of sunlight becomes visible as it passes through dust particles in the air of a room. Tyndall effect can also be observed when sunlight passes through the canopy of a dense forest. Here, tiny water droplets in the mist scatter sunlight.
We have just studied the spectrum of sun’s white light which consists of seven coloured lights. It we look at the spectrum of white sunlight, we will observe that the reds and blues are very' pre dominant in it. Red coloured light has a longer wavelength but the blue coloured light has a shorter wavelength. In fact, the wavelength of blue light is almost half that of the red light. In 1859, in an attempt to explain the blue colour of the sky, Tyndall discovered that when white light consisting of seven colours is passed through the clear liquid having small suspended particles in it, then the blue colour of white light having shorter wavelength is scattered much more than the red colour having longer wavelength.
Blue light has shorter wavelength, so it is scattered more easily. On the other hand, red light has longer wavelength, so it is not scattered much. In other words, the blue coloured light present in white sunlight is scattered much more easily than the red light. In fact, the blue light present in sunlight is scattered 10 times more than the red light.
Why blue colour of the sky appears dark to the astronauts in space
The sunlight scatters, when enters the earth’s atmosphere. The scattering of light in the earth’s atmosphere is due to the presence of atoms, molecules. Droplets and dust particles etc. the intensity of scattered light is more for the colour of less wave length. Since the wavelength of blue colour is less than the wave length of red colour, so blue colours scatters more than the red colour. Hence, sky appears blue to an astronaut standing on the earth. When the astronaut is in space, then there is no atmosphere (or atoms, molecules, droplets and dust particles) around him. Therefore, sun light does no scatter and hence sky appears dark.
Why planets do not twinkle
Plants are much closer to Earth than a star. Hence we get the intensity of light from The planet is huge. Therefore, the variation in the brightness of the planets is not detected. That's why the planets don't twinkle............












0 Comments