Spherical mirror:-the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is curved in words or out words. in fact, a spherical mirror is that mirror whose reflecting surface is a part of a hollow sphere of glass .one side of the mirror is well polished and reflecting, and Other Side Of the Mirror is opaque often painted red
Spherical Mirrors are of two types
concave mirror and
convex mirror
 |
| Fig1.1 |
1 concave mirror:-concave mirror is that spherical mirror in which the reflecting surface is towards the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part, eg, reflection of light occurs at concave surface or the bent in surface ,The Other surface of the concave spherical mirror is opaque or non reflecting as shown in Fig 1.1
2 Convex mirror:-Convex mirror is that spherical mirror in which the reflecting surface is away from the centre of the sphere ,of which the mirror is a part .Reflection of light occurs at convex surface or the bulging out surface ,The Other surface of the convex spherical mirror is opaque or non reflecting it is shown shaded, the inner shining surface of a steel spoon serves as a concave mirror and the outer shining surface of the steel spoon serves as convex mirror
 |
| Fig1. 1 |
Centre of curvature, Pole ,Radius of curvature, Principal axis, Aperture
of spherical mirror,
Centre of curvature:-Centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is the centre of the hollow sphere of glass of which the spherical mirror is a part .the centre of curvature is usually represented by letter C. in other word centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies in front of the mirror and centre of curvature of a convex mirror lies at the back of the mirror.
Pole:- the pole of a spherical mirror is the centre of the mirror and not the centre of the sphere . the pole is usually represented by the letter P. Note that pole of a spherical mirror is also called vertex of the mirror.
 |
Radius of curvature:- the radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of which the spherical mirror is a part .the radius of curvature is usually represented by the letter R
Principal axis:- The principal axis of a spherical mirror is the straight line passing through the centre of curvature c and pole P of the spherical mirror , produced on both sides the line xx' is the principal axis of a concave mirror.
Aperture:-the aperture of a spherical mirror is the diameter of the reflecting surface of the mirror it is also called linear aperture off the mirror it is the portion of the mirror from which the reflection of light actually takes place.
Principal focus and focal length of a concave mirror
Principal focus :-The principal focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principal axis of the mirror at which rays of light incident on the mirror in a direction parallel to the principal Axis actually meet after reflection from the mirror the principal focus of a concave mirror is represented by the letter f parallel rays falling on the concave mirror get reflected and meet actually at F therefore the principal focus f of a concave mirror is a real point it lies always in front of the concave mirror
Focal length:-Focal length of a concave mirror is the distance of a principal focus F of the mirror from the pole P of the mirror it is represented by letter f thus PF =f= focal length of a concave mirror
Principal focus and focal length of a convex mirror
The principal focus of a convex mirror, is a point on the principal axis of the mirror ,from which rays of light incident on the mirror in a direction parallel to the principal Axis appear to diverge. after reflecting from the mirror the principal focus of a convex mirror is represented by the letter F. Focal length of a convex mirror is the distance of the principal focus F of the mirror from the pole P of the mirror it is represented by the letter f
thus PF = f = focal length of a convex mirror
Sign conventions for spherical mirror
In a ray diagram of concave as well as convex spherical mirror we use new cartesian sign conventions for measuring various distances these signs are as under
1 the principal axis of the mirror is taken along x axis of the rectangular co-ordinate system and pole P of the mirror is taken as origin
2 the object is taken on the left side of the mirror
3 All the distances parallel to the principal axis of the spherical mirror are measured from the pole of the mirror
4 The distance measured in the direction of the incident light are taken as positive
5 The distance measured in a direction opposite to the direction of the incident light are taken as negative
6 The heights measured upward above the x axis and perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror are taken as positive
7 The heights measured downward and perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror are taken as negative as shown in
figure
Rules for tracing images formed by concave mirror
When an object is placed in front of the concave mirror its image is formed by reflection in the mirror every point on the object acts like a point source from which an infinite number of Rays originate in order to locate the image of the point object we take only two lines into consideration and the image formation takes place after following certain rules these rules are as under
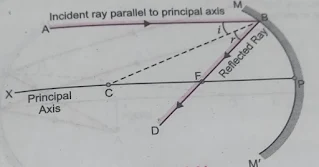
Rule1:- Ray of light falling on a concave mirror in a direction parallel to the principal axis of the mirror passes actually to the the principal focus of the mirror on a reflecting from the mirror. As shown in fig
Rule 2 :-A Ray of light incident on a concave mirror on passing through centre of curvature of the mirror is reflected back along the same path eg such a Ray retraces its path in opposite direction
as shown in fig
Rule3:-Ray of light incident on the concave mirror on passing through the focus of the mirror become parallel to principal axis of the mirror on reflection as shown in fig
Rule 4:- A Ray of light incident obliquely towards the pole P of a concave mirror is reflected obliquely as per the laws of reflection as shown in fig
FOR FIRST PART PLEASE CLICK ON THE BELOW LINK
https://jkgovtschoolnotes.blogspot.com/2022/01/class-10-physics-light-reflection-and.html
FOR THIRD PART PLEASE CLICK ON THE BELOW LINK
https://jkgovtschoolnotes.blogspot.com/2022/01/class-10-th-light-3rd-blog.html

















0 Comments