Ashaq Hussain Bhat
Teacher School Education
Department Jammu and Kashmir
ACIDS BASES AND SALTS
INTRODUCTION OF
The two main sources of most of the chemical substances
(1) Animals and plants
(2) Minerals and rocks
The chemical substance obtained from animals and Plants living organisms) are called organic compounds whereas those obtained from minerals and rocks are called inorganic compounds. These compounds are present in the food stuff as well as in a number of other materials that we use in everyday life like washing soda, lime etc, The earliest classification of inorganic compounds, including a large number of organic compounds, was on the basis of their taste. On this basis, the compounds were classified into the following three categories :
(i) Acids
(ii) Bases and
(iii) Salts
Acids are the substances which have sour taste. The term has been derived from the Latin word, acidus, which means sour. A few examples of acidic substances used in everyday life include lemon juice, tomatoes, vinegar etc.
Bases are the substances which have bitter taste. A few examples of substances having basic nature include washing soda, baking soda etc.
Salts are the compounds formed from acids and bases. A few examples of the salts include sodium chloride, copper sulphate, silver nitrate, calcium carbonate etc. Salts having taste similar to that of common salt are called salty.
However, some salts have very unpleasant taste and even may be poisonous. Hence, it is very dangerous to taste any chemical substance. You are therefore, advised never to taste any chemical substance.
Indicators for testing acids and bases:
- An indicator is a 'dye' that changes colour when it is put into an acid or a base. An indicator gives different colours in acids and bases. Thus, an indicator tells us whether the substance we are testing is an acid or a base by change in its colour. In other words, an indicator tells us whether the substance we are testing is acidic or basic by change in its colour. The three common indicators to test for acids and basses are: Litmus, Methyl orange and Phenolphthalein.
The most common indicator used for testing acids and basses in the laboratory is litmus. Litmus can be used in the form of litmus solution or in the form of litmus paper. It is of two types: blue litmus and red litmus.
An acid turns blue litmus to red.
A base (or alkali) turns red litmus to blue.
So, a convenient way to find out whether a solution is acidic or basic is to test it with litmus and observe the change in colour which takes place. Litmus is a natural indicator. Its neutral colour is purple. It is made into blue litmus and red litmus for the sake of convenience in detecting colour change when an acid or base is added to it.
Methyl orange is a synthetic indicator. Its neutral colour is orange. It turns to red in acids but yellow in bases.
Phenolphthalein is also a synthetic indicator. Its neutral colour is colourless. It remains colourless in acids but turns pink in bases.
Note:- Turmeric and red cabbage leaves are also natural indicators. Turmeric turns red in bases. Red cabbage leaves remain red in acids but turn green in bases.
Note :- Those substances whose smell changes in acidic or basic solutions are called olfactory indicators. Onion and vanilla are olfactory indicators. When basic solutions are added to olfactory indicators, its smell cannot be detected. However, the acidic solutions do not affect their smell.
Note:- The indicators like litmus, methyl orange, turmeric and phenolphthalein can tell us whether the given substance is an acid or a base but it cannot tell us whether the substance is a strong or a weak acid or a strong base or a weak base. For this purpose universal indicator is used. Universal indicator is a mixture of many different indicators which gives different colours at different pH values of the entire pH scale. The different colours and the corresponding strength of the solutions are given below:
1) Red (strong acids)
( 2) orange (weak acid)
(3) green (neutral)
( 4) blue (weak base)
(5) violet (strong base).
ACIDS: - Those chemical substances which are sour in taste are called acids. These substances ionize (dissociate) on dissolving in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+ aq ions). Acids are classified into organic acids and mineral acids.
The acids present in plant materials and animals are called organic acids. These exist in nature. Acetic acid, oxalic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid lactic acid and formic acid are some examples of organic acids. These acids are weak acids.
The acids obtained from minerals of the earth are called mineral acids. These are man-made acids. Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid are three common mineral acids. Concentrated mineral
acids are very dangerous (strong). They can burn our hands and clothes. Carbonic acid is also a mineral acid but very weak
Note:- A common thing in all acids is that they produce hydrogen ions (H+ aq ions] when dissolved in water acid but it is very weak.
Note:- Hydrogen ions exist as hydronium ions [H3O+] when in solution.
Note: All the compounds containing hydrogen are not acids. For example, glucose is not an acid though it contains hydrogen.
Note: - Sources of some of the organic acids are: Acetic acid (vinegar), Lactic acid (sour milk or curd), Oxalic acid (tomato), Citric acid (lemon and orange), Tartaric acid (tamarind and grapes) and formic acid (ant sting)
How will you show that all the compounds containing hydrogen are not acids?
The solutions of glucose, alcohol, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid contain hydrogen. Fix two nails on a cork and place it in a beaker. Connect the nails to the two terminals of a battery through a switch and a bulb. Pour some dilute hydrochloric acid in the beaker and switch on the current. The bulb starts glowing. This shows that hydrochloric acid solution conducts electricity. Now repeat this process by taking sulphuric acid solution in the beaker. The bulb will again glow showing that sulphuric acid solution also conducts electricity. If the process is repeated by taking glucose solution and alcohol solution separately in the beaker, the bulb will not glow. This shows that these compounds do not conduct electricity and as such are not acids. Hence all hydrogen containing compounds are not acids. As shown in Fig
Note:- Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it does not contain any ionic compound (like acids, bases or salts) dissolved in it.
Note:- Rain water conducts electricity because while falling to the earth it dissolves carbon dioxide (acidic oxide) from the air and forms carbonic acid. This carbonic acid provides hydrogen ions to conduct electricity.
How will you show that acids do not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
. Take some solid sodium chloride in a clean and dry boiling tube and add some concentrated sulphuric acid to it. Fix a rubber cork, with a small glass delivery tube, in the mouth of the tube. Concentrated sulphuric acid reacts with sodium chloride to form hydrogen chloride gas. This gas starts coming out of the open end of the glass tube. Hold a "dry" blue litmus paper in this gas. There is no change in the colour Of the paper Now hold a "moist "Blue litmus paper in the gas, this time the colour of the paper changes to red, this shows that hydrogen chloride gas shows acidic behaviour in the presence of water
Properties of Acids -
(1)They have sour taste.
(2) They turn blue litmus to red but the red litmus remains unaffected.
(3) They are electrolytes.
(4) They react with metals to form hydrogen gas and a salt. For example, when zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, then zinc sulphate (salt) and hydrogen gas are produced.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4+Hz.
5) They react with metal carbonates and metal bicarbonates (hydrogen carbonates) to form salt, carbon dioxide and water. For example, when dilute hydrochloric acid combines with sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate, then sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and water are formed:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + CO2 + H2O
NaHCO3 + HCl + NaCl + CO2 + H2O
On passing the carbon dioxide gas evolved through lime water, it turns milky because of the formation of a white precipitate of calcium carbonate:
Ca (OH)2+ CO2 → CaCO, + H20.
On passing excess carbon dioxide through lime water, then white precipitate formed first dissolves because of the formation of a soluble salt calcium bicarbonate, and the solution becomes clear again:
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O + Ca(HCO3)2.
6) They react with bases (or alkalies) to form salt and water. For example, when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide solution, then sodium chloride and water are formed:
NaOH + HC → NaCl + H2O.
7) They react with metal oxides to form salt and water. For example, cupric oxide combines with dilute
hydrochloric acid to form cupric chloride and water:
CuO + 2HCI ---- > CuCl2 + H2O.
SOME INTERESTING FACTS
(a) Limestone, chalk and marble are different forms of the same chemical calcium carbonate.
(b) It is not harmful to eat or drink substances containing organic acids.
(c) While diluting concentrated acids, acids should be added to water rather than adding water to acts because the heat evolved during the process will be easily absorbed by water. If water is added to the acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns.
(d) If someone is suffering from acidity after overeating, he should take baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) because it reacts with excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach and neutralizes it. Thus the person gets relieved
(e) Egg-shells contain calcium carbonate.
(f) The reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization reaction. Similarly, the reactions between metal oxides and acids and between metal hydroxides and acids are also neutralization reactions.
(g) Metal oxides and metal hydroxides are basic in nature.
(h) The antacid called "milk of magnesia" is a metal hydroxide. It is used to remove indigestion due to presence of too much hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
(i) Mineral acids are corrosive in nature as such these are not stored in metal containers. It is because of this reason that curd and sour substances are not kept in metal containers. These are stored in glass and ceramic containers.
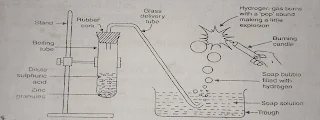
How will you test that hydrogen gas is produced when an acid reacts with a metal?
A. Take few pieces of zinc granules in a boiling test tube and add about 5ml of dilute sulphuric acid to it. The formation of gas bubbles is observed on the surface of zinc granules. Pass the gas being cred through the soap solution. Gas filled bubbles are formed in the soap solution which rise into the air. Now bring a burning candle near a gas filled soap bubble. A pop sound is produced. The pop sound produced shows that hydrogen gas is produced during the reaction,
Strong bases: A base which Ionizes completely in water and thus produces large amount hydroxide ions (OH' ions) , is called a strong base, Sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are examples of strong bases
Weak Bases: A base which ionizes partially in water and thus produces a small amount of hydroxide ions(OH ions) is called a weak base. Calcium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide are examples of weak bases.
Note:- A common property of all the bases is that they produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
Note:- Ammonium hydroxide is a base though it is not a metal hydroxide.
Note:- Metal carbonates and bicarbonates, neutralize acids and are thus considered as bases
Note:- Soluble bases (alkalis) are much more useful than insoluble bases
Properties of Bases:-
1) They have bitter taste.
2) They feel soapy to touch.
3) They turn red litmus to blue.
4) They are electrolytes.
5)They react with some metals to form hydrogen gas. For example, when sodium hydroxide is heated with zinc, then sodium zincate and hydrogen gas are formed:
2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2.
6)They react with acids to form salts and water. For example, when sodium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid, then sodium sulphate and water are formed:
2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H20.
7)They react with non-metal oxides to form salt and water. For example, calcium hydroxide solution reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate and water:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O.
How will you show that hydrogen gas is produced when bases combine with metals?
A. Take few pieces of zinc granules in a boiling test tube and add about 5ml of sodium hydroxide solution to it. Heat the tube. The formation of gas bubbles is observed on the surface of zinc granules. Pass the gas being evolved through the soap solution. Gas filled bubbles are formed in the soap solution which rise into the air. Now bring a burning candle near a gas filled soap bubble. A pop sound is produced. The pop sound produced shows that hydrogen gas is produced during the reaction.
STRENGTH OF ACID AND BASE SOLUTIONS:-
In 1909 Sorenson devised a scale on which the strength of acid solutions as well as basic solutions could be represented by making use of hydrogen ion concentrations in them. This scale is called pH scale. On this scale Sorenson linked the hydrogen ion concentrations of acid and base solutions to the numbers from 0 to 14. In the term pH, letter 'p stands for a German word 'potenz' which means 'power and letter stands for hydrogen ion concentration. pH is a pure number, it has no units. The pH of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of hydrogen ions in it. This means higher the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, lower will be its pH whereas lower the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution, higher will be its pH.
According to the rules of pH scale: As shown in Fig
(1)Neutral substances have a pH of exactly 7. Pure water; sugar solution and sodium chloride solution have pH = 7 because they are neutral substances.
(2)Acidic solutions have a pH of less than 7. More acidic a solution is, the lower will be its pH. For example, a solution of pH 1 is a stronger acid than another solution of pH 5.
(3)Basic solutions or alkaline solutions have a pH of more than 7. More basic a solution is, higher will be its pH. For example, a solution of pH 14 is a stronger base than another solution of pH 9.
The common pH scale having pH values from 0 to 14 is given on the figure above.
Importance of pH in everyday life:-
(1)pH in our digestive system:- Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid which helps in the digestion of food without harming our stomach. During indigestion the stomach produces too much acid which causes pain and irritation. To get rid of this pain, people use antacids (bases). These antacids neutralize the excess acid and the person feels relieved.
Note:- Antacids (anti-acids) are a group of mild bases which do not have toxic effects on the body. For example, magnesium hydroxide and sodium bicarbonate.
(2)pH change as the cause of tooth decay:- Tooth decay starts when the pH of the mouth is lower than 5.5 because at this pH the tooth enamel is corroded. The pH in the mouth is reduced to below 5.5 when the bacteria present in the mouth produce acids by degrading sugar and food particles left in the mouth after eating. The best way to prevent this is to clean the mouth properly after eating food
Note:- Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in the body. It is made up of calcium phosphate.
Note:- Cleaning teeth with toothpaste prevent tooth decay because these are generally basic. It has pH of nearly 8.
(3)Plants and animals are sensitive to pH changes:- The pH plays a very important role in the survival animals, including human beings. Our body works well within a narrow pH range of 7 to 7.8. If, due some reason, this pH range gets disturbed in the body of e person, then many ailments can occur. For Example, when acid rain flows into the rivers, it lowers the pH of the river water. Too much acid rain can lower the pH of river water to such an extant that the survival of aquatic animals becomes difficult. Most of the plants grow best when the pH of the soil is close to 7. If the pH of the soil is too low or too high then the plants do not grow well or do not grow at all. By adding chemicals to the soil its ph can be adjusted such that it becomes suitable for growing crops.
SOME INTERESTING FACTS
(1)When pH of the rain water is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain.
(2)The pH of acidic soil can reach as low as 4 and that of the basic soil can go up to 8.3.
(3)If the soil is too acidic then it is treated with materials like quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) to reduce its acidity.
(4)If the soil is too basic then it is treated with organic matter like manure or compost to reduce its basic nature.
. How can we check the pH of the soil?
We can check the pH of the soil in our backyard by the following process:
(a) Put about 2 g of soil in a test tube and add about 5ml of water to it.
(b) Shake the contents of the tube.
(c) Filter the contents of the tube.
(d) Find the pH of the filtrate by using the universal indicator paper. This will give the pH of the soil.
Self defence by plants and animals through chemical warfare:-
Many plants and animals protect themselves from their enemies by injecting painful and irritating acids and bases into their skin. For example, when a honey-bee stings a person, it injects an acidic liquid into the skin which causes immense pain and irritation. By rubbing with a mild base like baking soda solution on this area, the person gets relief because, being a base, baking soda neutralizes the effect of the acidic liquid injected by the bee. Similarly, when a wasp stings, it injects an alkaline liquid into the skin which causes pain. By rubbing with a mild acid like vinegar on this area, the person gets relief because, being an acid, vinegar neutralizes the effect of the alkaline liquid injected by the wasp.
Some plants also give painful stings. For example, leaves of a wild plant (nettle) inject methanoic acid into the skin of the person causing pain. This effect can be neutralized by rubbing the area with a base
COMMON SALT (SODIUM CHLORIDE):-
The chemical name of common salt is sodium chloride. It is a neutral salt and its formulae is NaCl. It is also known as just "salt". It can be prepared in the laboratory by the combination of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O
Common salt occurs naturally in dissolved form in sea water and in solid form as rock salt.
Common salt is obtained from sea water by the process of evaporation. During this process sea water is trapped in large, shallow pools. Due to heat of the sun the water slowly evaporates and common salt is left behind.
The large crystals of common salt found in underground deposits are called rock salt. This is usually brown because of the presence of impurities. It was formed when the ancient seas dried up by evaporation, thousands of years ago.
sodium bicarbonate thus formed is only slightly soluble in water, so it precipitate out as a solid. It is Separated by filtration, dried and heated to form sodium carbonate
2 NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O.
The anhydrous sodium carbonate thus formed is dissolved in water and recrystallised to get crystals of washing soda:
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H20.
Uses of Washing soda:-
(1)It is used as a cleansing agent.
(2) it is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
(3) It is used in the manufacture of glass, soap, paper and borax.
BAKING SODA
Chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (sodium bicarbonate) and its formulae is
NaHCO3. It is produced by treating cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride with ammonia and
carbon dioxide:
NaCl + NH3 + CO2 + H2O -> NaHCO3 + NH4CI.
Uses of Baking soda:-
(1)It is used as an antacid to remove acidity of the stomach.
(2)It is used in making baking powder.
(3)It is used in fire extinguishers.
NOTE:- Baking soda is added to tartaric acid or (citric acid) to form baking powder. These two combine only in presence of water
BLEACHING POWDER
Chemical name of bleaching powder is calcium oxychloride and its formulae is CaoC12. it is also called chloride of lime, it is prepared by passing chlorine gas over dry slaked lime (calcium hydroxide):
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaoCl2 + H2O.
Uses of bleaching powder:-
1)It is used for disinfecting drinking water supply.
2)It is used for the manufacture of chloroform.
3)It is used for making wood unshrinkable.
4)It is used as an oxidising agent in many chemical industries.
5) it is used for bleaching cotton and linen in textile industry; bleaching wood pulp in paper industry and bleaching washed clothes in laundry.
PLASTER OF PARIS:-
Chemical name of plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate and its formulae is
CaSO4.0.5H2O.It is commonly known as P.O.P.
It is prepared by heating gypsum (CaSO4.2H20) to a temperature of 100°C in a kiln:
CaSO4.2H20 → CaSO4.0.5H20 + 1.5 H20.
Uses of plaster of Paris:-
(1) It is used in hospitals for setting fractured bones in the right position to ensure correct healing.
(2) It is used for making casts in dentistry.
(3) it is used in making toys, decorative materials; cheap ornaments, cosmetics, black-board chalk and casts for statues.
4) It is used as a fire-proofing material.
5) it is used for making surfaces of walls smooth before painting them.
6) It is used in laboratories for sealing air-gaps in apparatus.
NOTE:-Anhydrous calcium sulphate is also called dead burnt plaster.
NOTE:-Formulae of plaster of Paris is also written as 2CaSO4.H20.
NOTE:-P.O.P should be stored in moisture proof containers.
NOTE:-Gypsum is calcium sulphate dehydrate (CaSO4.2H20).
- WATER OF CRYSTALLISATION:-
The water molecules which form part of the structure of a crystal of a salt are called water of crystallization. It is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formulae unit of a sait. The salt which contains water of crystallization is called hydrated salt. Since water of crystallization is a part of "crystal structure” of a salt, it does not wet the salt. It gives shape and imparts colour to the salts.
Examples of hydrated salts are:
1) Copper sulphate crystals contain 5 molecules of water of crystallization and is written as Cu5045H20.
2) Gypsum crystals contain 2 molecules of water of crystallization and is written as CuSO4.2H20.
3) Washing soda contains 10 molecules of water of crystallization and is written as CuS0410H20.
4) iron sulphate contains 7 molecules of water of crystallization and is written as FeSO4.7H2O.
CLICK ON THIS LINK
https://jkgovtschoolnotes.blogspot.com/2022/03/how-client-was-saved-lesson-no-7.html













0 Comments